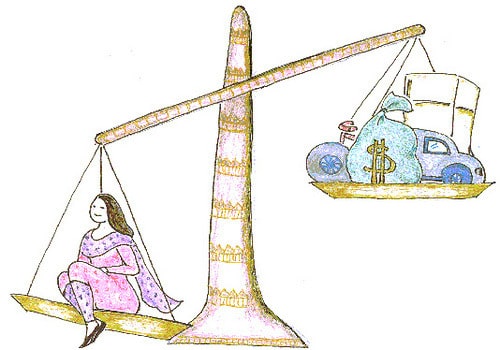
DOWRY
According to “The Dowry Prohibition Act,1961” Dowry means any property or valuable security given or agreed to be given either directly or indirectly by one party to a marriage to the other party to the marriage or by the parents of either party to a marriage or by any other person, to either party to the marriage or any other person; at or before or any time after the marriage in connection with the marriage of said parties but does not include dower or mahr in the case of persons to whom the Muslim personal law (Shariat) applied.
In layman’s language, In some cultures, the bride or her family pays a certain amount of money or property to the groom when a couple is married. This payment is called dowry.
The Indian law views dowry as a social evil that must be deracinated and finds its motive force in the principle that a girl child should not be considered a financial burden.
In India according to “The dowry prohibition Act”,
if any person gives or takes dowry shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than three or majorly five years with fine, not less than fifteen thousand rupees or the amount of value of such dowry or whichever is more.
If any person demands dowry from parents, relatives, or guardians of the bride or bridegroom, he shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which shall be not less than six months which may extend to two years, and with a fine which may extend to ten thousand.
If any person advertises/offers his property/ cash through any advertisements in any newspaper, periodical, journal, or any other media as consideration for the marriage or his son or daughter or circulates/prints any
advertisements, he shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than six months but which may extend to five years or with a fine which may extend to fifteen thousand rupees.